Planet Nine: A World That Shouldn't Exist
Nanoparticles present sustainable way to grow food crops

Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis hope that nanoparticle technology can help reduce the need for fertilizer, creating a...
U.S. Army Researchers Explore Future Rotorcraft Technologies

Artist’s conception of a future vertical lift aircraft concept.
Nanoparticles hold promise as double-edged sword against genital herpes

Zinc oxide tetrapod nanoparticles are shown.
Superfast light source made from artificial atom
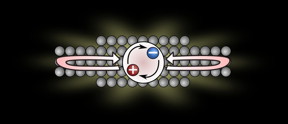
In a quantum dot, there are both negatively charged particles and positively charged particles that are missing electrons (also referred to...
Hubble Sees a Star 'Inflating' a Giant Bubble
New Ceres Images Show Bright Craters

Ceres' Haulani Crater, with a diameter of 21 miles (34 kilometers), shows evidence of landslides from its crater rim.
Lone Planetary-Mass Object Found in Family of Stars

A young, free-floating world sits alone in space in this illustration. The object, called WISEA J114724.10?204021.3, is...













