First population estimates EU population up to slightly over 510 million at 1 January 2016…… despite a first ever negative natural change
On 1 January 2016, the population of the European Union (EU) was estimated at 510.1 million, compared with 508.3 million on 1 January 2015. During the year 2015, almost 5.1 million babies were born in the EU, while more than 5.2 million persons died, meaning that the EU recorded for the first time ever a negative natural change of its population. The remainder of the change (positive) is driven mainly by net migration.
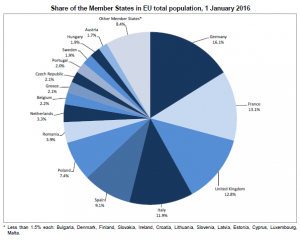
The most populated EU Member States continue to be Germany (82.2 million residents), France (66.7 million), the United Kingdom (65.3 million) and Italy (60.7 million). Together, they are home to more than half of the EU population.
These figures are issued by Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union, just before the World Population Day (11 July). Some other interesting facts and an infographic about the EU population are also published on the Eurostat website.
Population increase in seventeen Member States
During 2015, the population increased in seventeen EU Member States and decreased in eleven.
The largest increase was observed in Luxembourg (+23.3 per 1 000 residents), ahead of Austria (+14.4‰), Germany (+11.8‰), Malta (+11.7‰), Sweden (+10.6‰), Denmark (+8.4‰) and Belgium (+7.2‰).
In contrast, the largest decreases were recorded in Lithuania (-11.3‰), Latvia (-8.7‰) and Croatia (-8.2‰), followed by Bulgaria (-6.7‰), Greece (-6.0‰), and Romania (-5.6‰).
In total, the population of the EU increased by almost 2 million people (+3.5‰) during the year 2015. Germany, France and the United Kingdom with highest demographic weight Accounting for 16.1% of the total EU population at 1 January 2016, Germany continues to be the most populated Member State, ahead of France (13.1%), the United Kingdom (12.8%), Italy (11.9%), Spain (9.1%) and Poland (7.4%). For the remaining Member States, nine have a share of between 4% and 1.5% of the EU population and eleven a share below 1.5%.
Highest birth rates in Ireland, France and the United Kingdom, lowest in Italy, Portugal and Greece
During the year 2015, nearly 5.1 million babies were born in the EU, 40 000 fewer than the previous year. Across Member States, the highest crude birth rates in 2015 were recorded in Ireland (14.2 per 1 000 residents), France (12.0‰), the United Kingdom (11.9‰) and Sweden (11.7‰), while the lowest were registered in Italy (8.0‰), Portugal (8.3‰) and Greece (8.5‰). At EU level, the crude birth rate was 10.0 per 1 000 residents.
There were slightly over 5.2 million deaths registered in the EU in 2015, 286 000 more than the previous year. Bulgaria (15.3 per 1 000 residents) had in 2015 the highest crude death rate, followed by Latvia and Lithuania (both 14.4‰), Hungary (13.4‰) Romania (13.2‰) and Croatia (12.9‰). At the opposite end of the scale, Ireland (6.4‰), Cyprus (6.9‰) and Luxembourg (7.0‰) recorded the lowest. The crude death rate was 10.3 per 1 000 residents in the EU.
Consequently, Ireland (with a natural change of its population of +7.7‰) was in 2015 the Member State where births most outnumbered deaths, ahead of Cyprus (+3.9‰), Luxembourg (+3.7‰), France (+3.0‰), the United Kingdom (+2.7‰) and Sweden (+2.4‰). In contrast, among the thirteen EU Member States which registered a negative natural change in 2015, deaths outnumbered births the most in Bulgaria (-6.2‰), Croatia and Hungary (both -4.0‰), Romania (-3.8‰), Lithuania (-3.5‰) and Latvia (-3.3‰).
Geographical information
The European Union (EU) includes Belgium, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
Methods and definitions
Population change refers to the difference between the size of the population at the end and the beginning of the period. Specifically, it is the difference in population size on 1 January of two consecutive years. A positive population change is also referred to as population growth. A negative population change is also referred to as population decline. The population change consists of two components: natural change and net migration.
The natural change of population represents the difference between the number of live births and the number of deaths during the year. A positive natural change, also known as natural increase, occurs when live births outnumber deaths. A negative natural change, also named as natural decrease, occurs when live births are less numerous than deaths.
A crude rate is calculated as the ratio of the number of events to the average population of the respective area in a given year. For easier presentation, it is multiplied by 1 000: the result is therefore expressed per 1 000 persons (of the average population).
source: European Commission
- 517 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

