Science
First Wireless Charging Road to Be Activated in Los Angeles to Support the 2028 Olympics
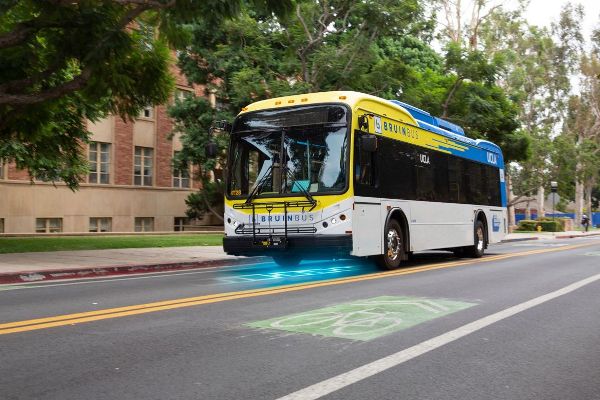

- Read more
- 137 reads
World's First Wooden Satellite Launched to Reduce Space Debris and Explore the Use of Wood in Space

- Read more
- 164 reads
H3 Rocket Launches with 'Kirameki-3' Satellite, Deploying Japanese Military Satellite into Operation

- Read more
- 140 reads
3.26 Billion Years Ago, Meteorite Impact Brought New Opportunities for the Evolution of Life on Earth

- Read more
- 131 reads
Human Rights
Visited:24,231,870
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020