Potential Threat in 2032: Asteroid Impact Probability Rises
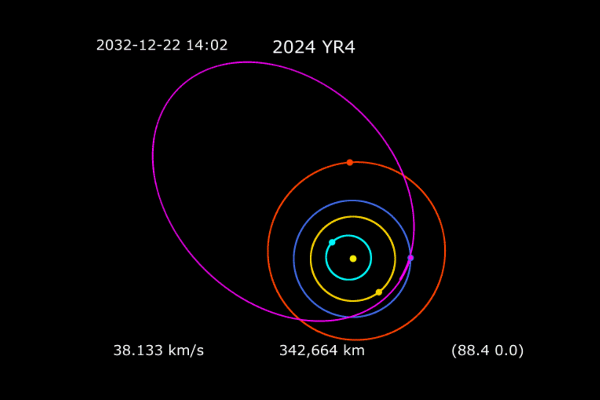
NASA's latest observations indicate that a potentially devastating asteroid, "2024 YR4," could collide with Earth in 2032, with the probability rising to 3.1%, marking the highest recorded risk in modern monitoring history. While experts believe there is no need for panic, they recommend close global monitoring and preparedness.
The asteroid was first observed on December 27, 2023, by the El Sauce Observatory in Chile. Based on reflectance spectroscopy analysis, scientists estimate its diameter to be between 40 and 90 meters, classifying it as a typical rocky asteroid rather than a metal-rich type. When its impact probability exceeded 1% on January 29, 2024, the International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN) promptly issued an alert.
A similar threat emerged in 2004 when the asteroid "Apophis" was initially estimated to have a 2.7% chance of striking Earth in 2029, though subsequent observations ruled out the risk. Experts from the European Space Agency (ESA) have stated that if the probability surpasses 10%, the IAWN will issue an official warning to help affected regions develop response plans.
Unlike the 10-kilometer asteroid that contributed to the extinction of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago, "2024 YR4" falls into the "city killer" category. While it would not cause a global catastrophe, an impact could still result in severe regional destruction. Traveling at an estimated speed of 64,000 km/h (40,000 mph), it would generate an immense impact force. If it enters Earth's atmosphere, the most likely outcome is an airburst, releasing energy equivalent to 8 megatons of TNT—over 500 times the power of the Hiroshima bomb.
Bruce Betts, a scientist from The Planetary Society, noted that if "2024 YR4" is at the upper end of its estimated size range, it could strike the ground directly, forming a crater. Current projections suggest potential impact zones spanning the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Arabian Peninsula. However, experts emphasize that there is no need for extreme measures, such as mass evacuations, at this stage.
NASA's 2022 "Double Asteroid Redirection Test" (DART) has already demonstrated the feasibility of altering an asteroid's trajectory using a spacecraft. The James Webb Space Telescope is set to begin observing "2024 YR4" next month to gather more data, further assess the risk, and develop possible countermeasures.
- 14 reads
Human Rights
Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

The Peace Bell Resonates at the 27th Eurasian Economic Summit

Declaration of World Day of the Power of Hope Endorsed by People in 158 Nations

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

