Molecular capsules: Glowing with promise
Fluorescence has widespread applications, helping researchers to understand issues in the fundamental sciences and develop practical materials and devices. Among the useful fluorescent compounds in development, capsule-shaped molecular architectures, which possess both strong fluorescent properties and a nanometer-sized cavity, are particularly promising.
Molecular cages and capsules can be prepared through a simple synthetic process called coordinative self-assembly. However, most of them are composed of precious metal ions such as palladium and platinum, and are non-emissive due to quenching by the heavy metals.
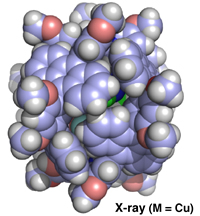
Crystal structure of the copper capsule
Now, Michito Yoshizawa, Zhiou Li, and co-workers from the Chemical Resources Laboratory at Tokyo Institute of Technology report novel molecular nanocapsules with the M2L4 composition (where M represents zinc, copper, platinum, palladium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese). Their zinc and copper capsules, in particular, display unique fluorescent properties.
The M2L4 capsules self-assemble from two metal ions and four bent ligands that include anthracene fluorophores (fluorescent parts). X-ray crystallographic analysis verified the closed shell structures where the large interior cavities of the capsules, around one nanometer in diameter, are shielded by eight anthracene panels.
The zinc capsule emitted strong blue fluorescence with a high quantum yield (80%), in sharp contrast to the weakly emissive nickel and manganese capsules and the non-emissive palladium, platinum, and cobalt capsules. The fluorescence of the copper capsule, on the other hand, depends on the solvent; for example, it shows blue emission in dimethyl sulfoxide but no emission in acetonitrile.
This study is the first to show such emissive properties of molecular capsules bearing an isolated large cavity. The researchers believe their nanocapsules could have novel applications in devices such as chemosensors, biological probes, and light-emitting diodes.
Source:Nanotechnology Now
- 329 reads




