IMF Executive Board Concludes 2017 Article IV Consultation with Brazil
On July, 5, 2017, the Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded the Article IV consultation with Brazil.
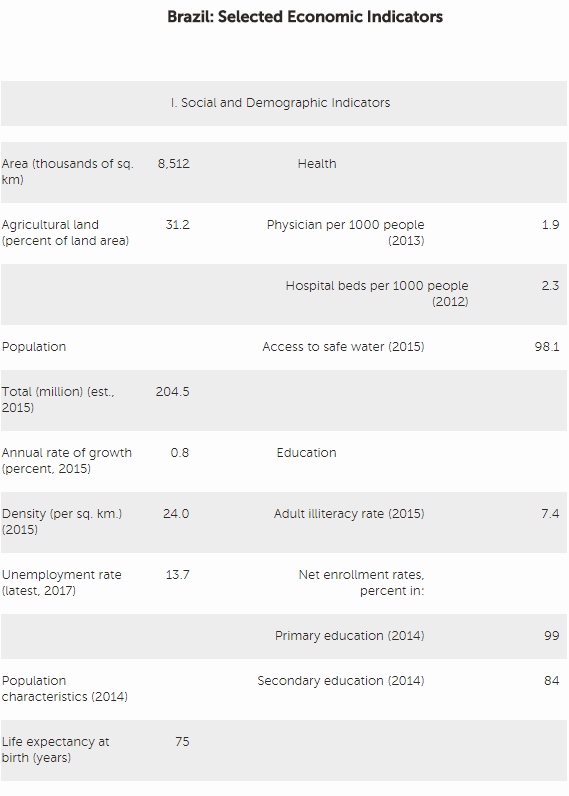
Brazil’s deep recession appears close to an end. The recession, triggered by large macroeconomic imbalances and a loss of confidence, was exacerbated by declining terms of trade, tight financing conditions, and a political crisis. Buoyed by congressional and market support, the new government has pursued an ambitious reform agenda. A constitutional amendment that caps growth in federal noninterest spending in real terms has been passed and progress has been made on the discussion of social security and other structural reforms. Recent indicators suggest Brazil’s economy is close to a turning point.
While the end of the recession appears to be in sight, a recent rise in political uncertainty has cast a shadow over the outlook. The government’s ability to deliver on social security reform, a necessary step toward securing fiscal sustainability, has become more uncertain—and, with national elections scheduled for 2018, the window for legislative action is closing.
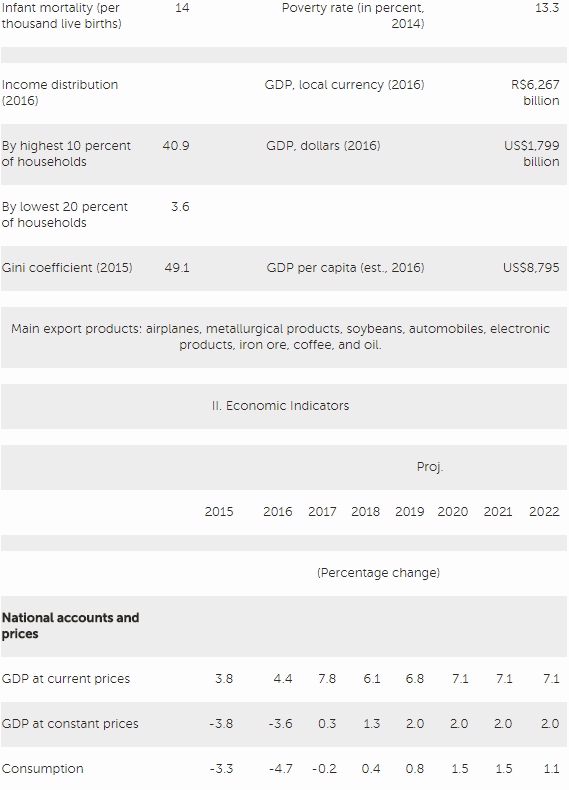
Fund staff expect a subdued recovery. Growth is projected to be 0.3 percent in 2017 and 1.3 percent in 2018, moving towards 2 percent in the medium term. Inflation is projected to undershoot its central target of 4.5 percent in 2017 and 2018. The forecast assumes that a sufficiently strong set of measures—most notably social security reform—are put in place to ensure fiscal sustainability. Political instability and spillovers from the corruption investigation are major sources of risk that could threaten the reform agenda and the recovery. The main policy risk is that the social security reform is severely diluted or delayed to the next government, prompting adverse market reaction in the near term and necessitating additional fiscal measures over time. The main external risks are a faster than expected tightening of global financial conditions and, with a lower likelihood, a significant slowdown in China.
Disinflation has continued, providing more room for monetary easing. After almost 2 years of being above the ceiling of the central bank’s tolerance range of 6.5 percent, inflation has declined rapidly over the past year. The impact of large increases in regulated prices in 2015 has dissipated, while a widening output gap, an appreciating exchange rate, declining inflation expectations, and a favorable shock to food prices have combined to speed disinflation since late 2016. The central bank began an easing cycle in September 2016, bringing the monetary policy rate down by a cumulative 400 bps to 10.25 percent as of June 2017. The National Monetary Council has announced a gradual reduction in the inflation target to 4.25 percent in 2019 and 4.0 in 2020, which will bring Brazil closer into line with other inflation targeting countries.
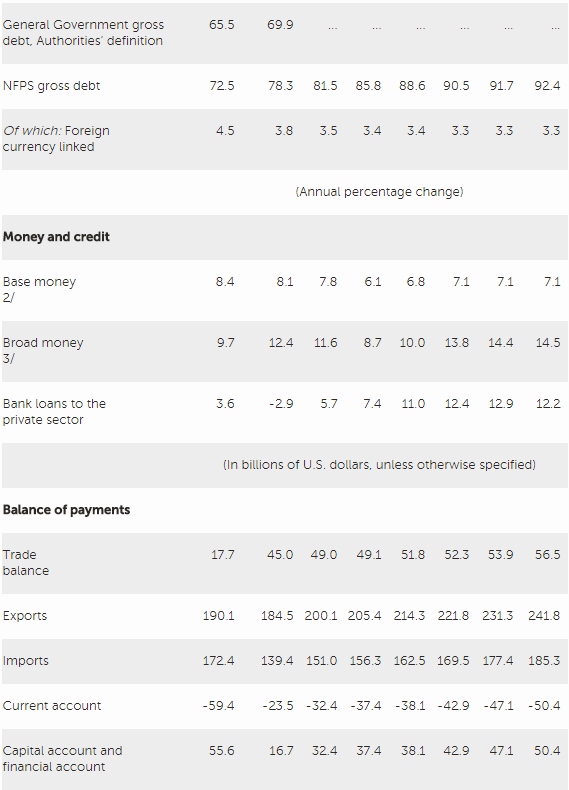
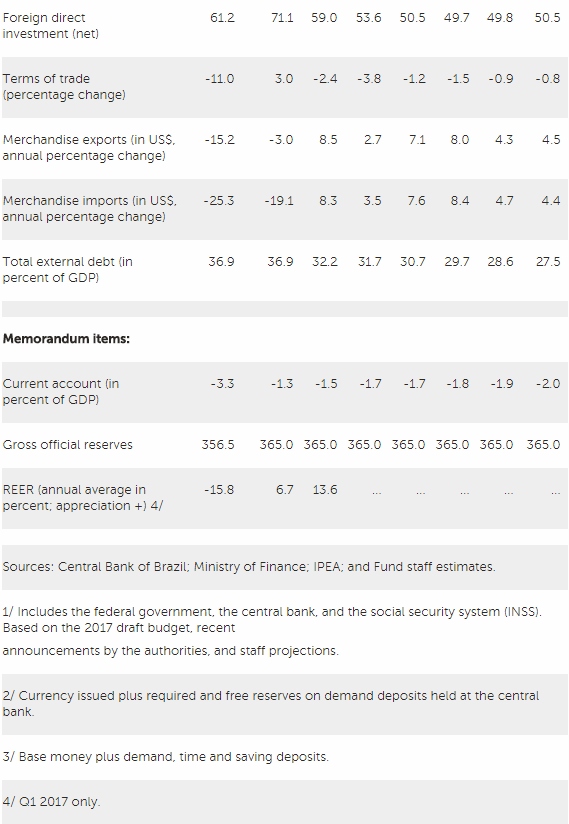
The recession has been a main driver of external adjustment. Reflecting weak investment and improving terms of trade, the current account deficit narrowed to 1.3 percent of GDP in 2016 (from 3.3 percent of GDP in 2015). On average in 2016, the external position was broadly consistent with medium-term fundamentals and desirable policies. Brazil has continued to attract sizeable capital inflows.
The flexible exchange rate has been an important shock absorber. The central bank reduced the rollover rate of maturing FX swaps and auctioned reverse FX swaps, significantly reducing its net forward position to 1.4 percent of GDP from over 5 percent of GDP at end-2015. International reserves have remained a source of strength, standing at US$365 billion at end-2016, above the IMF’s adequacy metric and other standard indicators.
The health of the banking sector has improved. Despite the recession, profits before taxes have surged due to high interest margins and lower funding costs. To limit increases in non-performing loans, banks have continued renegotiating the terms of loans and writing off delinquent loans. Capital ratios have increased on the back of a decline in private banks’ risk-weighted assets and higher unrealized gains on fixed income securities. Liquidity has also improved as withdrawals of saving deposits stopped and banks’ holdings of liquid assets increased. Overall external funding exposure and net open positions have remained low.
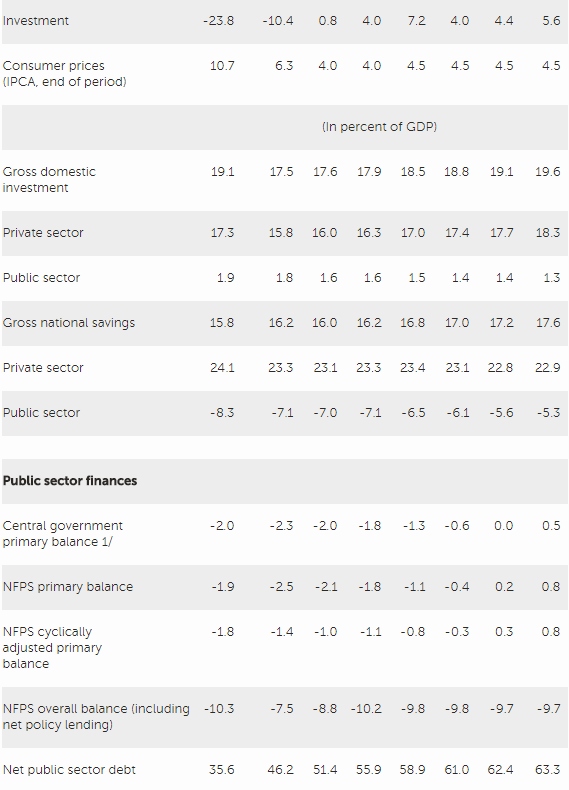
Fiscal outcomes have been disappointing and public debt ratios have risen sharply. Non-financial public sector debt rose from 72.5 percent of GDP to 78.3 percent between 2015 and 2016, with primary balances of -1.9 and -2.5 percent of GDP, and overall balances of -10.3 and -9.1 percent of GDP in those two years. The deficits in the primary balance have been largely the result of trend increases in mandatory spending and a sharp cyclical revenue downturn, while high borrowing costs and the contraction in output have delivered adverse debt dynamics.
The government aims to restore fiscal sustainability by gradually bringing primary balances toward surplus territory, with the support of the constitutional expenditure ceiling and social security reform. For 2017, the authorities aim to bring the primary deficit to ‑2.1 percent of GDP. They have introduced adjustment measures of 0.9 percent of GDP, including cuts in discretionary spending of 2/3 percent of GDP and a partial roll-back of payroll tax exemptions.
Executive Board Assessment
Executive Directors welcomed that the Brazilian economy is showing signs of recovery following years of deep recession. However, Directors noted that the recent rise in political uncertainty poses risks to the outlook and the government’s reform agenda. They emphasized that continued sound policies and ambitious structural reforms are needed to support macroeconomic stability, secure confidence, and anchor strong and durable growth.
Directors underscored that ensuring fiscal sustainability is a key priority. In this regard, they commended the authorities’ ambitious consolidation and reform efforts aimed at securing the sustainability of the public finances and social security. Directors welcomed the focus on controlling expenditure growth, including through the implementation of a cap on non interest federal expenditure. However, they highlighted that further efforts are needed to achieve fiscal targets. In light of the challenges facing the economy, Directors generally supported the current pace of fiscal adjustment, but emphasized that the fiscal effort will need to be more intense as the recovery takes hold. A rolling medium term fiscal framework would be helpful to clarify and update the government’s debt stabilization goals.
Directors highlighted the need to reform the social security schemes, including those for civil servants at all levels of government, in view of unfavorable demographic trends and large actuarial imbalances. They also noted the importance of this reform for the federal spending cap over time. Directors expressed concern over subnational finances, and encouraged the authorities to continue developing durable solutions in coordination with the states.
Directors agreed that monetary policy has been appropriately calibrated and recommended continuing monetary easing. Nevertheless, they encouraged continuous reassessment of the policy stance in view of the evolution of inflation and expectations and prospects for fiscal reforms. Directors welcomed the efforts to strengthen Brazil’s inflation targeting framework through improved communications and steps to alleviate distortions in credit markets.
Directors underscored that the floating exchange rate system and reserve buffers are key sources of strength for Brazil and should be preserved. They commended the reduction in foreign exchange intervention and recommended that interventions be limited to addressing disorderly market conditions.
Directors observed that the financial sector has remained sound despite the severe stresses. To make the system more robust, they encouraged actions to further strengthen financial safety nets through enhanced monitoring and an improved crisis management framework. Directors underscored the need for continued vigilance and close monitoring of the health of the corporate sector and its impact on the banking system.
Directors stressed that ambitious structural reforms, including in the areas of tax policy, labor markets, and infrastructure are essential to raise long term growth. They also underscored the importance of trade reforms to enhance competitiveness and efficiency. Directors noted the ongoing efforts to combat corruption and stressed that continued strong action to improve governance, increase transparency and strengthen institutional frameworks will be key to securing strong, durable and inclusive growth.
Source: International Monetary Fund
- 324 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

