IMF Executive Board Concludes 2017 Article IV Consultation with Malaysia
On March 15, 2017, the Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded the Article IV consultation with Malaysia.
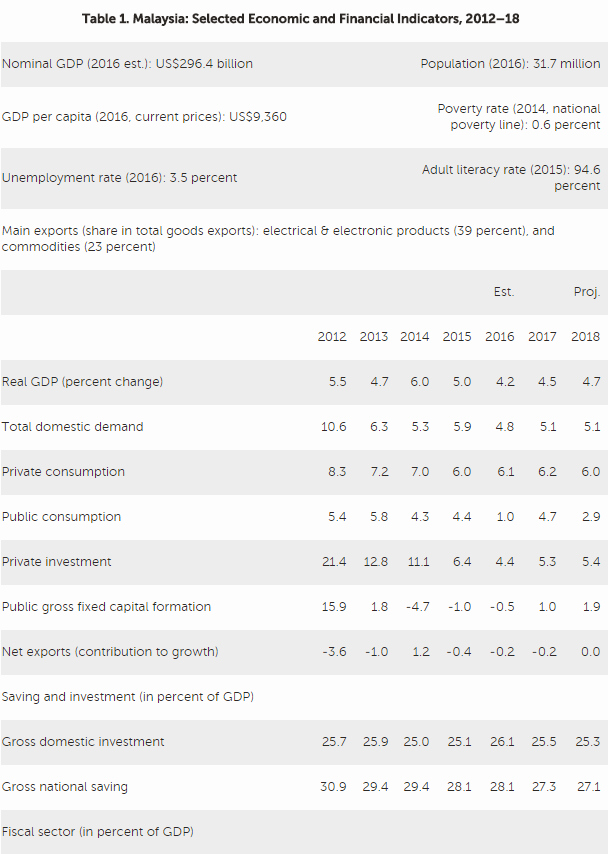
Despite a challenging global economic environment, the Malaysian economy performed well over the past few years. Notwithstanding the impact of the global commodity price and financial markets volatility, the economy remained resilient, owing to a diversified production and export base; strong balance sheet positions; a flexible exchange rate; responsive macroeconomic policies; and deep financial markets. While real GDP growth slowed down, Malaysia is still among the fastest growing economies among peers. The challenging global macroeconomic and financial environment puts premium on continued diligence and requires careful calibration of policies going forward.
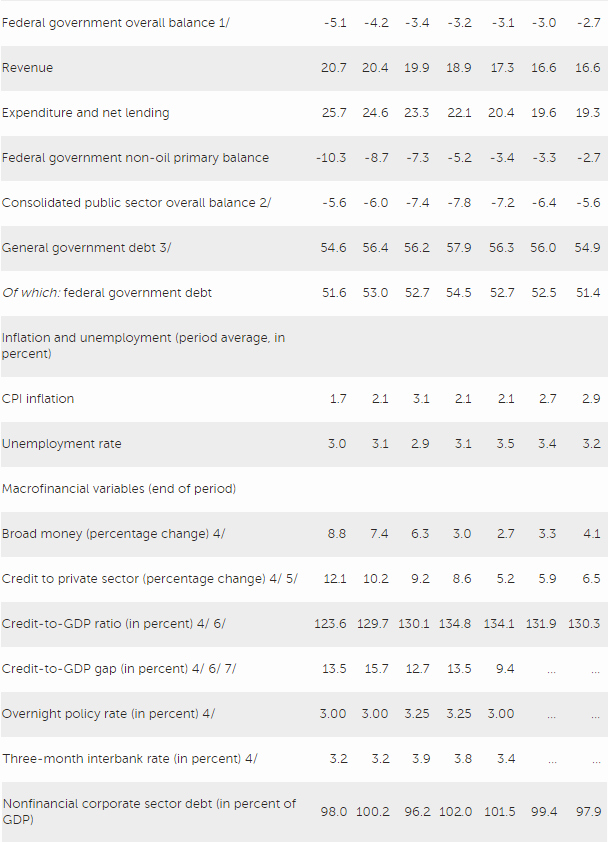
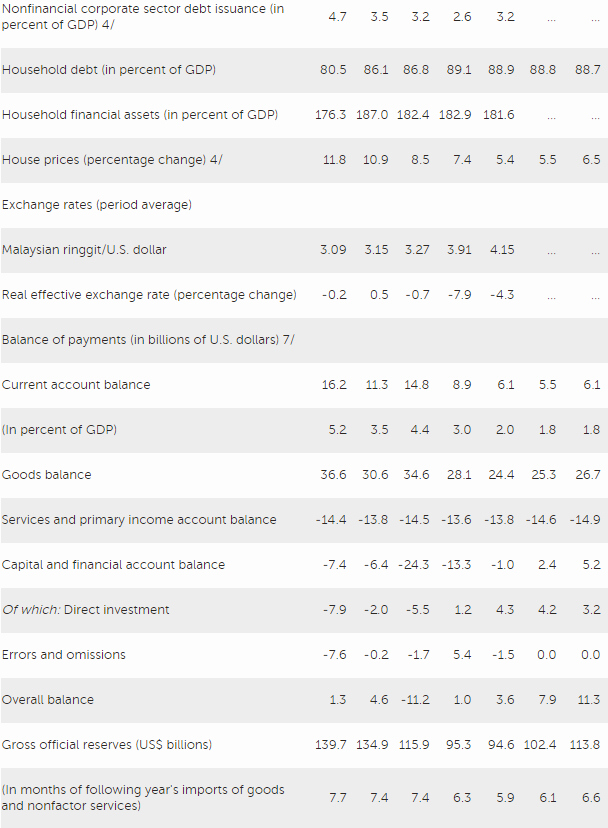
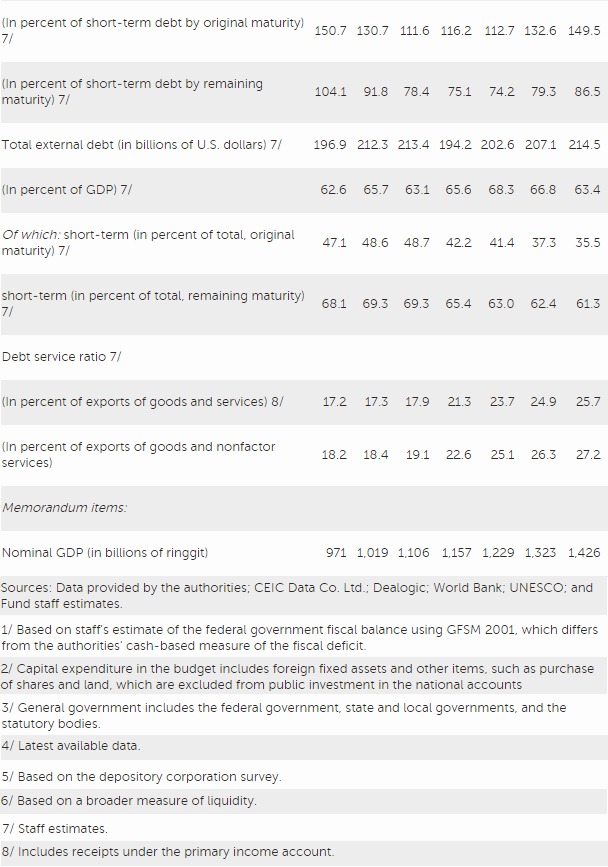
Risks to the outlook are tilted to the downside, originating from both external and domestic sources. External risks include structurally weak growth in advanced and emerging market economies and retreat from cross-border integration. Although the Malaysian economy has adjusted well to lower global oil prices, sustained low commodity prices would add to the challenge of achieving medium-term fiscal targets. Heightened global financial stress and associated capital flows could affect the economy. Domestic risks are primarily related to public sector and household debt, along with pockets of vulnerabilities in the corporate sector. Federal debt and contingent liabilities are relatively high, limiting policy space to respond to shocks. Although the household debt-to-GDP ratio is likely to decline, household debt also remains high, with debt servicing capacity growing only moderately.
Real GDP growth rate is expected to increase moderately to 4.5 percent year-on-year (y/y) in 2017 from 4.2 percent in 2016. Domestic demand, led by private consumption, continue to be the main driver of growth, while a drag from net exports, similar to 2016, will remain. Consumer price
inflation is projected to rise and average 2.7 percent y/y in 2017 on the back of higher global oil prices and the rationalization of subsidies on cooking oil. The current account surplus would be largely unchanged as impacts from an improved global outlook and higher commodity prices would be offset by the strength of imports on the back of a resilient domestic demand.
Executive Board Assessment
Executive Directors commended the resilience of the Malaysian economy, which reflects sound macroeconomic policy responses in the face of significant headwinds and risks. While Malaysia’s economic growth is expected to continue in 2017, weaker-than-expected growth in key advanced and emerging economies or a global retreat from cross-border integration could weigh on the domestic economy. Against this background, Directors urged vigilance and continued efforts to strengthen policy buffers and boost long-term economic growth.
Directors agreed that the authorities’ medium-term fiscal policy is well anchored on achieving a near-balanced federal budget by 2020. The planned consolidation will help alleviate risks from elevated government debt levels and contingent liabilities and build fiscal space for future expansionary policy, as needed. Directors recommended that the pace of consolidation reflect economic conditions and that any counter-cyclical fiscal policy measures be well-targeted and temporary. They noted that improvements to the fiscal framework, such as elaborating medium-term projections and preparing and publishing an annual fiscal risks statement, would help anchor medium-term fiscal adjustment and mitigate risks.
Directors agreed that the current monetary policy stance is appropriate. Going forward, Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) should continue to carefully calibrate monetary policy to support growth while being mindful of financial conditions. Directors emphasized that global financial market conditions could affect the monetary policy space and should be carefully monitored.
Directors noted that the banking sector is sound overall and that financial sector risks appear contained. Nonetheless, they cautioned that potential pockets of vulnerability should be closely monitored. They noted that household debt remains relatively high, while in the corporate sector, there are emerging vulnerabilities in some sectors. Directors suggested that macroprudential measures be adjusted if needed.
Directors underscored the central role of macroeconomic policy and exchange rate flexibility in helping the economy adjust to external shocks. In this regard, they welcomed the authorities’ commitment to keeping the exchange rate as the key shock absorber. They recommended that reserves be accumulated as opportunities arise and deployed in the event of disorderly market conditions. Noting the authorities’ aim to improve the functioning of the onshore forward foreign exchange market, Directors urged the BNM to monitor the effects of the recent measures introduced in this regard, recognizing their benefits and costs. They emphasized that close consultation and communication by BNM with market participants will be essential in further developing the foreign exchange market and bolstering resilience.
Directors underscored that steadfast implementation of the authorities’ ambitious structural reform agenda is key to boosting long-term economic potential. They supported the emphasis on increasing female labor force participation, improving the quality of education, lowering skills mismatch, boosting productivity growth, encouraging research and innovation, and upholding high standards of governance.
Source: International Monetary Fund
- 276 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

