Zika infection during pregnancy may disrupt fetal oxygen supply

A female Aedes mosquito.
Hold the salt: gut reaction may impair the brains of mice
We are often warned of the dangers of high levels of salt in our diet, yet the risks of salt consumption and the effects of salt on the body, including the brain, are not entirely clear. In a new mouse study, scientists link changes in the gut caused...
Memory gene goes viral
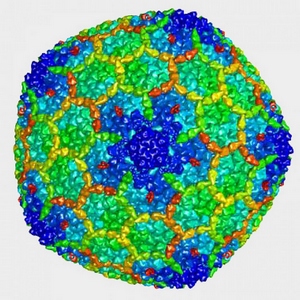
Memory gene acts like a virus: Two independent teams of NIH-funded researchers discovered that the Arc gene...
New study offers insights on genetic indicators of COPD risk
Researchers have discovered that genetic variations in the anatomy of the lungs could serve as indicators to help identify people who have low, but stable, lung function early in life, and those who are particularly at risk for chronic obstructive...
Scientists synthesize nanoparticle-antioxidants to treat strokes and spinal cord injuries
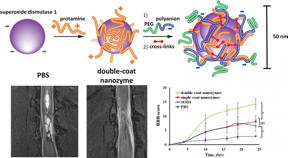
An international science team has developed an innovative therapeutic complex based on multi-layer polymer nano-structures of superoxide...
Bangladesh: UN agencies working to vaccinate half a million children against diphtheria

UNICEF is on the ground in Bangladesh, immunizing Rohingya refugee children to fight...
The coming of age of gene therapy: A review of the past and path forward
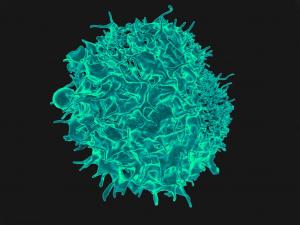
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a T lymphocyte. The engineering of lymphocytes, white blood cells...
NIH study shows steep increase in rate of alcohol-related ER visits
The rate of alcohol-related visits to U.S. emergency departments (ED) increased by nearly 50 percent between 2006 and 2014, especially among females and drinkers who are middle-aged or older, according to a new study conducted by researchers at the...
'Decorated' stem cells could offer targeted heart repair
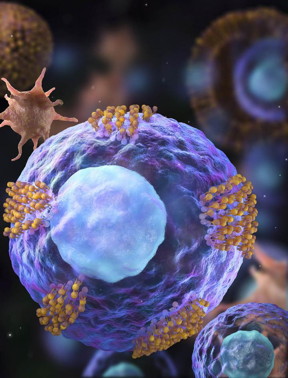
Cardiac stem cells (magenta) are decorated with platelet vesicles (brown).
Iodine deficiency may reduce pregnancy chances, NIH study suggests
Women with moderate to severe iodine deficiency may take longer to achieve a pregnancy, compared to women with normal iodine levels, according to a study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health. The study is the first to investigate the...











