Science
NASA'S Hubble Space Telescope Finds Dead Stars 'Polluted' With Planet Debris

Hubble found the building blocks for Earth-sized planets in an unlikely place – the atmospheres of a pair of burned-out stars called white dwarfs.
- Read more
- 381 reads
Second and Third Sounding Rockets Launched from the Marshall Islands

A NASA Terrier-Improved Orion sounding rocket leaves the launch pad at Roi Namur, the Republic of the Marshall Islands, as part of the Equatorial Vortex Experiment (EVEX). The rocket was launched 90 seconds after a Terrier-Oriole sounding rocket as part of a study of post-sunset solar storms.
- Read more
- 366 reads
Milky Way Black Hole Snacks on Hot Gas

This artist's concept illustrates the frenzied activity at the core of our Milky Way galaxy. The galactic center hosts a supermassive black hole in the region known as Sagittarius A*, or Sgr A*, with a mass of about four million times that of our sun. The Herschel space observatory has made detailed observations of surprisingly hot gas that may be orbiting or falling toward the supermassive black hole.
- Read more
- 402 reads
Furnace accelerator startup develops anti-fogging technology

After one hour and 19 minutes, there is no fog on the area of the visor where VitreOx has been applied.
- Read more
- 434 reads
Penn Research Makes Advance in Nanotech Gene Sequencing Technique
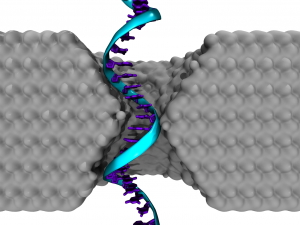
An illustration of a single-stranded DNA homopolymer translocating through a silicon nitride nanopore.
- Read more
- 496 reads
NASA's Fermi, Swift See 'Shockingly Bright' Burst

The maps in this animation show how the sky looks at gamma-ray energies above 100 million electron volts (MeV) with a view centered on the north galactic pole. The first frame shows the sky during a three-hour interval prior to GRB 130427A. The second frame shows a three-hour interval starting 2.5 hours before the burst, and ending 30 minutes into the event. The Fermi team chose this interval to demonstrate how bright the burst was relative to the rest of the gamma-ray sky. This burst was bright enough that Fermi autonomously left its normal surveying mode to give the LAT instrument a better view, so the three-hour exposure following the burst does not cover the whole sky in the usual way.
- Read more
- 341 reads
'Going negative' pays for nanotubes: Rice University lab finds possible keys to better nanofibers, films
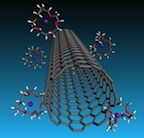
Crown ether “cages” trap potassium ions but leave nanotubes with a repellant negative charge in solutions that will be valuable for forming very strong, highly conductive carbon nanotube fibers. The Rice University discovery appears in ACS Nano.
- Read more
- 379 reads
How graphene and friends could harness the Sun’s energy

- Read more
- 525 reads
China Receives US$95 Million Grant to End Production of Ozone-Depleting Global-Warming Gases to help Meet its Targets under the Montreal Protocol
China, the world's largest producer of hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC), received a US $95 million grant on April 23, 2013 to help reduce its production of HCFCs. These substances, used primarily in refrigeration and air-conditioning and in the manufacture of foam products, deplete the ozone layer and exacerbate climate change. The grant is from the Multilateral Fund for the Implementation of the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, which provides the funds in exchange for verified annual reductions of HCFC production levels.
- Read more
- 371 reads
'Tis the Season -- for Plasma Changes at Saturn

This is an artist's concept of the Saturnian plasma sheet based on data from Cassini magnetospheric imaging instrument. It shows Saturn's embedded "ring current," an invisible ring of energetic ions trapped in the planet's magnetic field.
- Read more
- 336 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

