Science
NASA Evaluates Four Candidate Sites for 2016 Mars Mission

The process of selecting a site for NASA's next landing on Mars, planned for September 2016, has narrowed to four semifinalist sites located close together in the Elysium Planitia region of Mars. The mission known by the acronym InSight will study the Red Planet's interior, rather than surface features, to advance understanding of the processes that formed and shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system, including Earth.
- Read more
- 486 reads
Penn develops computer model that will help design flexible touchscreens
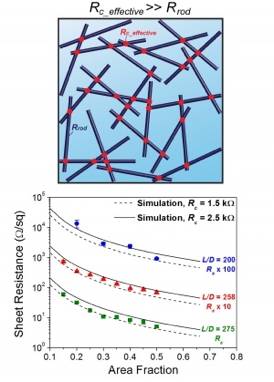
Researchers simulate electrical resistances (lines) to match experimental data (points) and extract the contact resistance.
- Read more
- 391 reads
Engineers make golden breakthrough to improve electronic devices
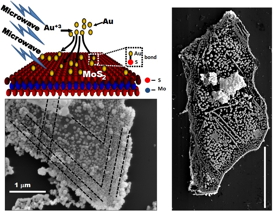
Vikas Berry, William H. Honstead professor of chemical engineering, and his research team have studied a new three-atom-thick material -- molybdenum disulfide -- and found that manipulating it with gold atoms improves its electrical characteristics.
- Read more
- 350 reads
Bizarre Alignment of Planetary Nebulae

Astronomers have used ESO's New Technology Telescope and the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope to explore more than 100 planetary nebulae in the central bulge of our galaxy. They have found that butterfly-shaped members of this cosmic family tend to be mysteriously aligned — a surprising result given their different histories and varied properties.
- Read more
- 472 reads
Production of Multi-Layer Titania Nanotube Arrays with Application in Advanced Medicine

- Read more
- 539 reads
Measuring progress in nanotech design
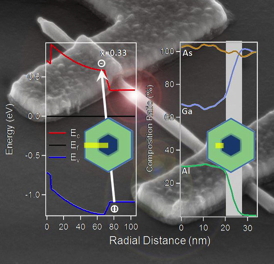
Tracking a nanowire device's photocurrent responses, created by varying the wavelengths of a laser, will allow Drexel researchers to make measurements and adjustments that could help them design more efficient and smaller components for smartphones, laptops and even solar panels.
- Read more
- 350 reads
Biodegradable Nanofibrous Scaffold Designed for Cell Growth, Tissue Recovery
- Read more
- 353 reads
Creating a 'window' to the brain: University of California, Riverside researchers develop novel transparent skull implant that could provide new treatment options for disorders such as brain cancer and traumatic brain injury
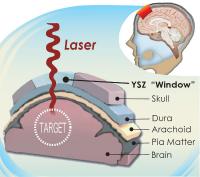
This is an illustrated cross section of the head that shows how the transparent skull implant works.
- Read more
- 358 reads
Blue Light Observations Indicate Water-Rich Atmosphere of a Super-Earth

Artist's rendition of a transit of GJ 1214 b in blue light. The blue sphere represents the host star GJ 1214, and the black ball in front of it on the right is GJ 1214 b.
- Read more
- 385 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020


