Health
4,500 children under the age of five died from measles in the Democratic Republic of the Congo so far this year
“Since the beginning of the year, more than 5,000 people have died due to measles, over 90 per cent of them children under the age of five.
- Read more
- 326 reads
Investigational Drugs Reduce Risk of Death from Ebola Virus Disease
The investigational therapeutics mAb114 and REGN-EB3 offer patients a greater chance of surviving Ebola virus disease (EVD) compared to the investigational treatment ZMapp, according to published results from a clinical trial conducted in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The new report also shows that early diagnosis and treatment are associated with an increased likelihood of survival from EVD.
- Read more
- 313 reads
Head-to-head comparison finds three anti-seizure drugs equally effective for severe form of epilepsy
There are three treatment options commonly used by doctors in the emergency room to treat patients with refractory status epilepticus, severe seizures that continue even after benzodiazepine medications, which are effective in controlling seizures in more than two-thirds of patients. New findings that the three drugs, levetiracetam, fosphenytoin, and valproate, are equally safe and effective in treating patients with this condition. The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health.
- Read more
- 348 reads
Innovative WHO HIV testing recommendations aim to expand treatment coverage
The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued new recommendations to help countries reach the 8.1 million people living with HIV who are yet to be diagnosed, and who are therefore unable to obtain lifesaving treatment.
- Read more
- 348 reads
Pediatric drug trial finds benefit in teens with heart defect
Teenagers born with a single working ventricle of the heart — a rare defect that cannot be completely corrected — showed a significant improvement in their ability to sustain moderate exercise after treatment with udenafil, a drug that helps improve blood flow, according to a new study.
- Read more
- 278 reads
Cerebral organoid model provides clues about how to prevent virus-induced brain cell death
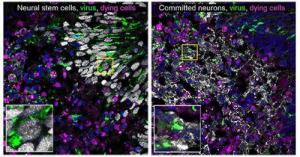
These images taken from LACV-infected cerebral organoids show infected cells (green) and cells that are dying from infection (magenta). The left image also shows neural stem cells (white) that have the potential to become neurons; these cells are rarely dying. In contrast, the image on the right shows committed neurons (white), many of which are shown to be dying.
- Read more
- 318 reads
High amounts of screen time begin as early as infancy, NIH study suggests
Children’s average daily time spent watching television or using a computer or mobile device increased from 53 minutes at age 12 months to more than 150 minutes at 3 years, according to an analysis by researchers at the National Institutes of Health, the University at Albany and the New York University Langone Medical Center. By age 8, children were more likely to log the highest amount of screen time if they had been in home-based childcare or were born to first-time mothers.
- Read more
- 337 reads
UN agencies ramp up Somalia measles and polio campaign

Two children play in the surf on Mogadishu's Lido beach.
- Read more
- 295 reads
Decline in Early Childhood Obesity in WIC Families
In a new study, 41 U.S. states and territories show significant declines in obesity among children, aged 2-4 years, from low-income families enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) between 2010-2016, according to data published on Nov. 21.
- Read more
- 280 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020


