Science
Designing climate-friendly concrete, from the nanoscale up: New understanding of concrete’s properties could increase lifetime of the building material, decrease emissions

The left and center diagrams show the structure of cement hydrate as determined by the researchers’ model, which calculates the positions of particles based on particle-to-particle forces. Each simulation box is about 600 nanometers wide. The packing fraction (the fraction of the box occupied by particles) is assumed to be 0.35 in the left diagram and 0.52 in the center one. Open pores, indicated by the white areas, are more prevalent at the lower packing fraction. The right-hand diagram is a sketch of cement hydrate published by T.C. Powers in 1958.
- Read more
- 302 reads
A 'smart dress' for oil-degrading bacteria
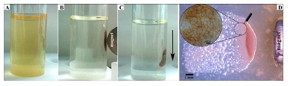
(a,b) Targeted movement of magnetic cells was facilitated by external magnetic field (in liquid media); (c) sedimentation of magnetically concentrated cells; (d) targeted movement and growth of magnetic cells on solid surface (inset shows a higher-magnification view of cells arranged on the surface).
- Read more
- 340 reads
New remote-controlled microrobots for medical operations

Scientists at EPFL and ETHZ have developed a new method for building microrobots that could be used in the body to deliver drugs and perform other medical operations.
- Read more
- 277 reads
Physicists collide ultracold atoms to observe key quantum principle

University of Otago physicist Niels Kjærgaard and his team have used extremely precisely controlled laser beams to confine, accelerate and gently collide ultracold atomic clouds of fermionic potassium.
This allowed them to directly observe a key principle of quantum theory, the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
This principle predicts a forbidden zone along a meridian of the spherical halo of scattered particles, which the Otago experiments indeed unveiled.
The dark band in the graphic shows a rule derived from the principle in action. This rule is that indistinguishable fermions cannot scatter out at 90 degrees to the collision axis.
- Read more
- 297 reads
Veggie juice that illuminates the gut: The medical imaging drink, developed to diagnose and treat gastrointestinal illnesses, is made of concentrated chlorophyll, the pigment that makes spinach green

A new University at Buffalo-led study suggests that chlorophyll-based nanoparticles are an effective imaging agent for the gut.
- Read more
- 328 reads
Germs add ripples to make 'groovy' graphene: New nanomaterial conducts differently at right angles

Atomic force microscopy image of a graphene sheet draped over a Bacillus bacterium (left). The bacterium is about 1 micron or 1/25,000 of an inch wide. After applying vacuum and heat treatment, regular wrinkles form in the graphene (right, at twice the magnification).
- Read more
- 320 reads
Astronomers find evidence for 'direct collapse' black hole

An image based on a supercomputer simulation of the cosmological environment where primordial gas undergoes the direct collapse to a black hole. The gas flows along filaments of dark matter that form a cosmic web connecting structures in the early universe. The first galaxies formed at the intersection of these dark matter filaments.
- Read more
- 436 reads
University of Illinois researchers demonstrate tunable wetting and adhesion of graphene

Doping-induced tunable wetting of graphene.
- Read more
- 381 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020



