Science
Chloroform cleanup: just the beginning for palladium-gold catalysts: Federally funded research pays off with new process for environmental remediation

When chloroform-contaminated water is flowed through a column containing PGClear pellets, the palladium and gold in the pellets spurs a chemical reaction that breaks down chloroform into nontoxic methane and chloride salt.
- Read more
- 368 reads
Where are the Best Windows Into Europa's Interior?

This graphic of Jupiter's moon Europa maps a relationship between the amount of energy deposited onto the moon from charged-particle bombardment and the chemical contents of ice deposits on the surface in five areas of the moon (labeled A through E).
- Read more
- 351 reads
U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Scientists “See” Flux Rope Formation for the First Time

Models of flux ropes have been drawn by theorists in the past, but scientists had never before observed them at the time they formed.
- Read more
- 383 reads
Blame it on the Rain (from Saturn's Rings)

This artist's concept illustrates how charged water particles flow into the Saturnian atmosphere from the planet's rings, causing a reduction in atmospheric brightness.
- Read more
- 370 reads
W3 star-forming region

The full image of the W3 region. Click on the image to see an annotated version, highlighting some of the key features.
- Read more
- 351 reads
Interdisciplinary team demonstrates superconducting qualities of topological insulators: Findings may prove useful in search for elusive Majorana quasiparticle
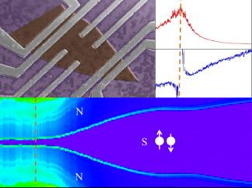
Top left: SEM image of a typical device. Mechanically exfoliated Bi2Se3 thin film is colored as brown and contact metals consist of Ti(2.5nm)/Al(140nm). Top right: Hall data where red curve is longitudinal resistivity and blue curve is Hall carrier density as a function of gate voltage. Bottom figure: 2D plot of differential resistance as a function of gate voltage(x axis) and current(y axis). Purple region in the center corresponds to zero differential resistance (superconducting regime)
- Read more
- 337 reads
Deep Space Applauds NASA Asteroid Initiative - Calls for Collaboration with Private Sector
- Read more
- 353 reads
Suzaku 'Post-mortem' Yields Insight into Kepler's Supernova

This composite of images from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory shows the remnant of Kepler's supernova in low (red), intermediate (green) and high-energy (blue) X-rays. The background is an optical star field taken from the Digitized Sky Survey. The distance to the object is uncertain, with estimates ranging from 13,000 to 23,000 light-years, but recent studies favor the maximum range. This image spans 12 arcminutes or about 80 light-years at the greatest distance.
- Read more
- 303 reads
Hubble Breaks Record in Search for Farthest Supernova

This is a Hubble Space Telescope view of supernova SN UDS10Wil, nicknamed SN Wilson that exploded over 10 billion years ago. The small box in the top image pinpoints SN Wilson's host galaxy in the CANDELS survey. The image is a blend of visible and near-infrared light. The three bottom images, taken in near-infrared light demonstrate how the astronomers found the supernova. The image at far left shows the host galaxy without SN Wilson. The middle image, taken a year earlier, reveals the galaxy with SN Wilson. The supernova cannot be seen because it is too close to the center of its host galaxy. To detect the supernova, astronomers subtracted the left image from the middle image to see the light from SN Wilson, shown in the image at far right.
- Read more
- 343 reads
NASA Flies Radar South on Wide-Ranging Expedition

On March 17, 2013, NASA's Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) acquired synthetic aperture radar data over the Napo River in Ecuador and Peru. The image colors indicate the likelihood of inundation (flooding) beneath the forest canopy, which is difficult to determine using traditional optical sensors.
- Read more
- 321 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

