Science
Elementary Physics in a Single Molecule
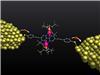
The molecule of about 2 nm in size is kept stable between two metal electrodes for several days.
- Read more
- 398 reads
NASA's WISE Finds Mysterious Centaurs May Be Comets

New observations from NASA's NEOWISE project reveal the hidden nature of centaurs, objects in our solar system that have confounded astronomers for resembling both asteroids and comets. The centaurs, which orbit between Jupiter and Neptune, were named after the mythical half-horse, half-human creatures called centaurs due to their dual nature. This artist's concept shows a centaur creature together with asteroids on the left and comets at right.
- Read more
- 336 reads
ALMA Sheds Light on Mystery of Missing Massive Galaxies

New observations from the ALMA telescope in Chile have given astronomers the best view yet of how vigorous star formation can blast gas out of a galaxy and starve future generations of stars of the fuel they need to form and grow. The dramatic images show enormous outflows of molecular gas ejected by star-forming regions in the nearby Sculptor Galaxy. These new results help to explain the strange paucity of very massive galaxies in the Universe.
- Read more
- 310 reads
Tropical Ecosystems Boost Carbon Dioxide as Temperatures Rise

Above image was made with the satellite instrument MODIS (or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data. It is a key instrument aboard the Terra (EOS AM) and Aqua (EOS PM) satellites.
- Read more
- 378 reads
UCSB study reveals mechanism behind squids' and octopuses' ability to change color

This shows the diffusion of the neurotransmitter applied to squid skin at upper right, which induces a wave of iridescence traveling to the lower left and progressing from red to blue. Each object in the image is a living cell, 10 microns long; the dark object in the center of each cell is the cell nucleus.
- Read more
- 335 reads
NYU-Poly Nano Scientists Reach the Holy Grail in Label-Free Cancer Marker Detection: Single Molecules
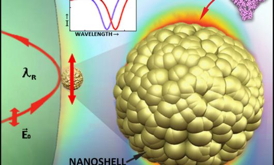
- Read more
- 386 reads
Curiosity Makes Its Longest One-Day Drive on Mars

The Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on NASA's Curiosity rover is carried at an angle when the rover's arm is stowed for driving. Still, the camera is able to record views of the terrain Curiosity is crossing in Gale Crater, and rotating the image 150 degrees provides this right-side-up scene. The scene is toward the south, including a portion of Mount Sharp and a band of dark dunes in front of the mountain. It was taken on the 140th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars, shortly after Curiosity finished a 329.1-foot (100.3-meter) drive on that sol. The drive was twice as long as any previous sol's drive by Curiosity.
- Read more
- 373 reads
NASA's Spitzer Observes Gas Emission From Comet ISON

These images from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope of C/2012 S1 (Comet ISON) were taken on June 13, when ISON was 310 million miles (about 500 million kilometers) from the sun.
- Read more
- 368 reads
A high-pressure nanoimaging breakthrough
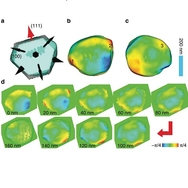
(a) Isosurface (30%) of the reconstructed amplitude superimposed with a model of the possible {111} and {100} crystal planes. The normal directions of two sets of crystalline planes {111} and {100} are marked by two kinds of arrows (fat and narrow), and the one (111) used for the measurement is marked in red. (b,c) are the top and bottom view of phase shift distribution pasted on the 30% isosurface plot. Three strain distinguished locations numerically labelled are chosen for quantitative measurement as a function of pressure. (d) 3D phase distribution at different slicing depths spaced apart by 20 nm steps from top to bottom of the crystal.
- Read more
- 432 reads
Direct nitrogen fixation for low cost energy conversion
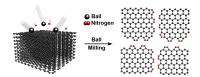
This is a diagram of Direct Nitrogen Fixation on Graphene Nanoplates.
- Read more
- 432 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

