Physicists from Bielefeld University have developed a new method of fabrication
In the future, carbon nanomembranes are expected to be able to filter out very fine materials. These separating layers are ultrathin, consisting of just one layer of molecules. In the long term, they could allow to separate gases from one another, for example, filtering toxins from the air.
More than ten years ago, Professor Gölzhäuser and his then team created the groundwork for the current development, producing a carbon nanomembrane from biphenyl molecules. In the new study, the process was altered so as to allow the use of other starting materials. The prerequisite is that these molecules are also equipped with several so-called phenyl rings. For their new method, the researchers use the starting material in powder form. They dissolve the powder to pure alcohol and immerse very thin metal layer in this solution. After a short time the dissolved molecules settle themselves on the metal layer to form a monolayer of molecules. After being exposed to electron irradiation, the monolayer becomes a cross-linked nanomembrane. Subsequently the researchers ensure that the metal layer disintegrates, leav-ing only the nanomembrane remaining. ‘Up until now, we have produced small samples which are are a few centimetres square', says Gölzhäuser. ‘However, with this process it is possible to make nanomembranes that are as big as square metres.'
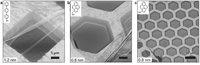
Using a new process the team working with Professor Dr. Armin Gölzhäuser has produced twelve different nanomembranes. The three images were made using the Bielefeld Helium Ion Microscope and show nanomembranes made from various starting materials.
This new method is so special because the researchers can produce made-to-measure nanomembranes. ‘Every starting material has a different property, from thickness or trans-parency to elasticity. By using our process, these characteristics are transferred onto the nanomembrane.' In this way, carbon nanomembranes can be produced to address many dif-ferent needs. ‘That was not possible before now', says Gölzhäuser.
Furthermore, graphene can be made from nanomembranes. Researchers worldwide are ex-pecting graphene to have technically revolutionising properties, as it has an extremely high tensile strength and can conduct electricity and heat very well. The conversion from nanomembranes into graphene is simple for the Bielefeld researchers: The membranes have to be heated in a vacuum at a temperature of about 700 degrees Celsius. Gölzhäuser's team is working on the project with physicists from Ulm University, Frankfurt University and the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research.
Source: Nanotechnology Now
- 431 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

