Ice-coated beauty in Mars’ Silver Island
On 8 June, the high-resolution stereo camera on Mars Express captured a region within the 1800 km-wide and 5 km-deep Argyre basin, which was created by a gigantic impact in the planet’s early history.

The image shows the western half of the 138 km-wide Hooke Crater, with wind formed dunes at its heart, while to the left of the crater, the ice-covered plains of Argyre Planitia are coated with a thin dusting of frozen carbon dioxide. The very large Argyre impact basin brought materials from the deeper martian crust and mantle to the surface.
After Hellas, the Argyre impact basin is the second largest on the Red Planet.
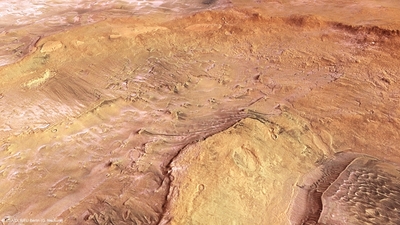
The lower right of the image shows the wind-formed dunes within Hooke Crater, while small deposits of frozen carbon dioxide ice lie within the crater, the top left of the image starts to show the more extensive ice lying on the surrounding Argyre Planitia.
The name stems from the Greek word ‘argyros’ (silver) and Argyre was an ‘island of silver’ in Greek and Roman mythology. Giovanni Schiaparelli, the famed Italian astronomer, gave the name to this bright region on Mars in his detailed 1877 map.
At the centre of the larger impact basin is a flat region known as Argyre Planitia. The Mars Express images in this release all show a portion of the northern part of this plain, with a large portion of each image dominated by the western half of the 138 km-wide Hooke Crater, named after the British physicist and astronomer Robert Hooke.

Hooke Crater and the surrounding Argyre Planitia are seen in broader context.
Most of Argyre Planitia has been shaped by wind, glacial and lacustrine (lake-based) processes, creating the smoother appearance of the landscape surrounding Hooke Crater.
Inside Hooke Crater itself, prevailing wind activity has formed dunes and helped to create linear erosion features, clearly seen in the following topographic image.

Topographical view Argyre Planitia
The most striking feature of this image release, shown clearly in the first image at the top of the page, is the icing sugar-like covering of the surface to the south (left) of the image. This is frost, but made of carbon dioxide, not water.
Carbon dioxide ice is commonly seen on the surface of Mars, and has long been thought to form only at ground level, freezing out of the atmosphere as frost, which is most likely the case here.

3D anaglyph view Hooke Crater
The lowlands to the south (left in the first image) of Hooke and regions within the crater are covered by a thin ice layer. However, it is lacking on the inner north-facing crater wall. It was probably melted there by the Sun, as indicated by the timing of the image.
Taken at around 4:30 in the local afternoon and during the southern hemisphere’s mid-winter, the Sun would have been just over 20 degrees above the horizon. It should then have been able to melt ice on the steeper north-facing slopes, but would probably not have had enough time to warm and melt any on low-lying horizontal surfaces.
Source: European Space Agency
- 388 reads
Human Rights
Fostering a More Humane World: The 28th Eurasian Economic Summi

Conscience, Hope, and Action: Keys to Global Peace and Sustainability

Ringing FOWPAL’s Peace Bell for the World:Nobel Peace Prize Laureates’ Visions and Actions

Protecting the World’s Cultural Diversity for a Sustainable Future

Puppet Show I International Friendship Day 2020

