US State to Quarantine Ebola-exposed Missionaries
The southern U.S. state of North Carolina is stepping up efforts to guard against the possible spread of the Ebola virus to the United States.
Women Who 'Lean In' Often Soon Leave Engineering Careers, Study Finds
Nearly 40 percent of women who earn engineering degrees quit the profession or never enter the field, and for those who leave, poor workplace climates and mistreatment by managers and co-workers are common reasons, according to research presented at...
Happier Consumers Can Lead to Healthier Environment, Research Reveals
The pursuit of true happiness can lead people to lifestyles that will not only be satisfying but will be better for the environment, according to an overview of psychological research presented at the American Psychological Association’s 122nd Annual...
U.S. emergency department visits for drug-related suicide attempts rise over six year period
Two new reports highlight the rise in drug-related suicide attempt visits to hospital emergency departments especially among certain age groups. The reports by U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) show that overall...
Exposure to Common Antibacterials May Affect Growth of Fetus: Study
UN declares Ebola outbreak global ‘international public health emergency’

In the Liberian capital Monrovia, a Ministry of Health employee sprays the sole of a colleague’s...
WHO Declares Ebola Outbreak a 'Public Health Emergency'
NIH and Italian scientists develop nasal test for human prion disease

The test developed by NIH and Italian scientists involves the insertion of a rigid fiber-optic rhinoscope into the patient’s...
Ebola Toll Tops 900; Liberia Declares Emergency
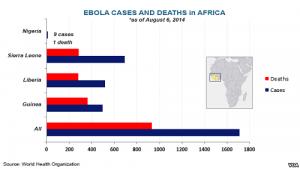
Ebola outbreaks, deaths in east Africa, as of August...
Year-round preventive treatment reduces malaria risk in young children
A year-round preventive drug treatment substantially reduces young children’s risk of contracting malaria and poses no serious risk of adverse events, according to a study by researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health.










